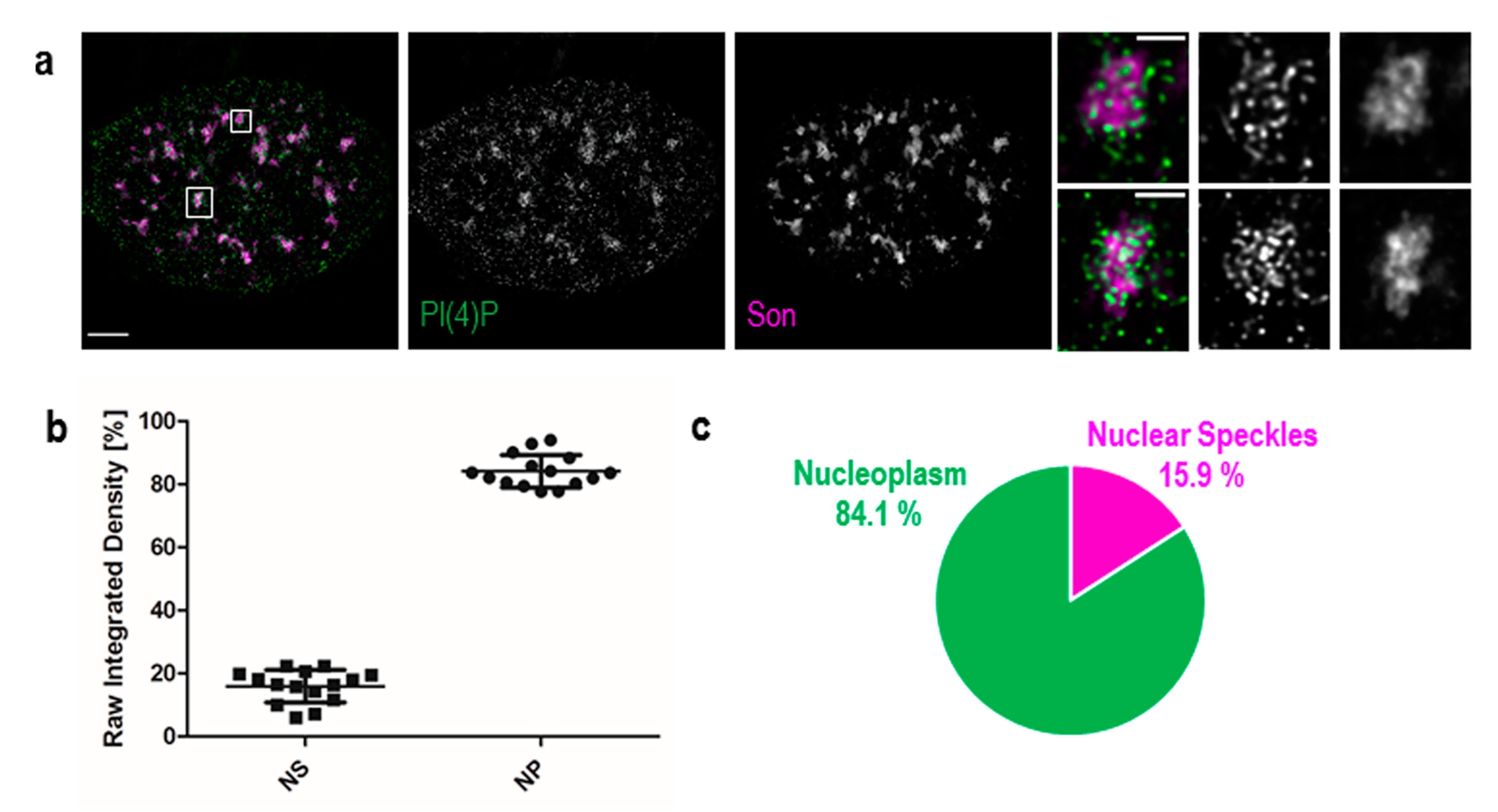
The nuclear lamina is attached to the inner nuclear membrane on the nucleoplasm.
What is nuclear lamina made of.
215 pathogenic mutations in lmna have been identified as causes.
The nuclear lamina is a component of the nuclear envelope whose major structural element is a mesh of type v intermediate filament proteins called lamins.
Two sets of intermediate filaments provide support for the nuclear envelope.
These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores.
The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes.
The increasing number of proteins that interact with lamins and the compound interactions between t.
An inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane.
The nuclear lamina is a dense 30 to 100 nm thick fibrillar network inside the nucleus of most cells it is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins besides providing mechanical support the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as dna replication and cell division additionally it participates in chromatin organization and it anchors the nuclear.
Specifically these proteins are located in the nuclear lamina a mesh like layer of intermediate filaments and other proteins that is attached to the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope.
Nuclear membrane the nuclear envelope sometimes called a nuclear membrane is a structure made of lipids that has the hereditary material of the eukaryotic cells.
It is the most interior component of the nuclear envelope located underneath the inner nuclear membrane.
An internal network forms the nuclear lamina on the inner nuclear membrane.
The nuclear lamina is made predominantly of intermediate filaments called lamins of which there are two main types.
A layer of proteins that gives strength and support to the nuclear membrane.
Type a and type b for a review see dechat et al 2008.
In mammals there are two major a type lamins lamin a and lamin c which are generated by alternative splicing of the lmna gene.
There are four major kinds of lamins which can be split into two types a and b types.
Lamins a and c are supporting scaffolding components of the nuclear envelope which is a structure that surrounds the nucleus in cells.
The nuclear lamina also connects to and anchors chromatins which are arranged loosely in dna and protein structure.
215 lamin a lmna is a principle component of the nuclear lamina that functions as a scaffolding molecule to assist in the organization of chromatin.
It is composed of lamins which are also present in the nuclear interior and lamin associated proteins.
The nuclear lamina is a dense fibrillar network of structural proteins that lines the inner nuclear membrane of eukaryotic cells.